Introduction to the Ichimoku Cloud
If you’re stepping into the world of forex trading, the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator is your formidable ally, capable of guiding you through the intricate realm of the foreign exchange market. Whether you’re a seasoned trader or just beginning your forex journey, mastering this powerful indicator can revolutionize your approach and elevate your trading success.
In this comprehensive guide, we will unravel the mystique surrounding the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator. We’ll embark on a journey to dissect its intricate components, demystify its inner workings, and equip you with a diverse array of strategies that hold the promise of catapulting your forex trading endeavors to new heights.
The foreign exchange market can often appear as an enigmatic sea of currencies in constant flux, and navigating it demands more than just a rudimentary understanding of charts and numbers. It necessitates a profound insight, an analytical edge, and an ally that can offer clarity amidst the chaos. The Ichimoku Cloud Indicator is precisely that ally, poised to illuminate your trading path, irrespective of whether you’re a novice or a seasoned trader.
As we embark on this comprehensive journey, envision the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator as your guiding star through the turbulent waters of forex trading. It’s a tool that can help you decipher market trends, identify critical entry and exit points, and ultimately, steer your trading vessel toward the shores of success. So, fasten your seatbelts, for this guide is your passport to unlocking the full potential of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator in the world of forex trading.
Understanding the Ichimoku Cloud
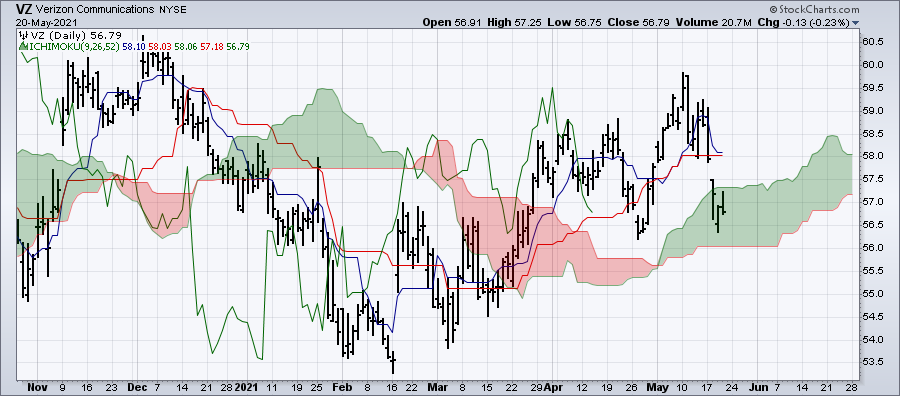
The Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, also known as Ichimoku Kinko Hyo, is a comprehensive technical analysis tool renowned for providing a holistic view of the forex market. Its multifaceted nature enables traders to gain profound insights into price movements, offering a distinct advantage in the world of forex trading. To unlock the full potential of the Ichimoku Cloud, it’s essential to delve into its key components, each contributing to a comprehensive analysis:
Tenkan Sen: The Conversion Line
The Tenkan Sen, often referred to as the Conversion Line, plays a pivotal role in the Ichimoku Cloud’s analytical framework. It is a short-term moving average calculated by averaging the highest high and the lowest low over a specific period, typically nine periods. The Tenkan Sen serves as a valuable tool for understanding short-term price momentum.
How to Use Tenkan Sen:
- Crossovers for Trend Reversals: One of its primary functions is to identify potential trend reversals. When the Tenkan Sen crosses above the Kijun Sen, it signals a potential bullish reversal. Conversely, when it crosses below the Kijun Sen, it indicates a potential bearish reversal.
- Assessing Trend Strength: The angle and steepness of the Tenkan Sen offer insights into the strength of the current trend. A steep upward slope suggests a strong bullish trend, while a steep downward slope indicates a robust bearish trend.
Understanding the Tenkan Sen is crucial as it helps traders make informed decisions about market entry and exit points, contributing to a well-rounded trading strategy. However, the Tenkan Sen is just one piece of the Ichimoku puzzle, and a comprehensive analysis requires considering the other components as well.
Now, let’s explore the Kijun Sen, another essential component of the Ichimoku Cloud, which complements the Tenkan Sen in providing a more comprehensive view of market trends and movements.
Kijun Sen
The Kijun Sen, often referred to as the Base Line, serves as another indispensable component within the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator. Unlike the Tenkan Sen, which provides a short-term perspective, the Kijun Sen offers a longer-term view of price movements. Calculated over a period of 26 periods, it plays a vital role in deciphering market dynamics and serves as both a support and resistance level.
How to Use Kijun Sen:
- Crossovers for Support and Resistance: One of the key applications of the Kijun Sen is in identifying potential areas of support and resistance. When the price interacts with the Kijun Sen, it can signify significant levels where price trends may reverse or encounter obstacles.
- A price crossing above the Kijun Sen suggests a potential upward move, indicating a support level.
- Conversely, a price crossing below the Kijun Sen implies a possible downward move, representing a resistance level.
- Analyzing Market Volatility: The distance between the Tenkan Sen and the Kijun Sen can provide valuable insights into market volatility. A wider gap between these lines suggests higher volatility, signifying substantial price swings. In contrast, a narrower gap indicates relatively lower volatility and more stable price movements.
Understanding the Kijun Sen’s role in the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator is essential for traders aiming to navigate the forex market successfully. It complements the insights gained from the Tenkan Sen, offering a broader perspective on price movements and helping traders identify critical support and resistance levels. As with any technical analysis tool, the Kijun Sen becomes even more powerful when used in conjunction with the other components of the Ichimoku Cloud.
Now, let’s explore the Chikou Span, another integral element of this comprehensive indicator, and understand how it contributes to a well-rounded analysis of forex market trends.
Senkou Span
In the intricate world of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, the Senkou Span holds a special place as it forms the foundation of the Kumo, the cloud-like area on an Ichimoku chart. The Kumo is a dynamic zone that plays a pivotal role in identifying potential areas of support and resistance. To comprehend the Senkou Span’s significance, it’s essential to delve into its components, Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B.
Senkou Span A: This component represents the average of the Tenkan Sen and Kijun Sen, and it’s projected 26 periods ahead on the chart. It offers insights into the mid-term equilibrium of price movements.
Senkou Span B: On the other hand, Senkou Span B is calculated by averaging the highest high and lowest low over the last 52 periods. Similar to Senkou Span A, it’s projected 26 periods ahead. Senkou Span B provides a longer-term perspective on market trends.
How to Use Senkou Span:
- Dynamic Support and Resistance: One of the primary applications of the Senkou Span is in defining dynamic support and resistance levels. These levels are represented by the upper and lower boundaries of the Kumo, formed by Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B, respectively. Traders often observe price interactions with the Kumo to identify potential areas where price trends may stall, reverse, or accelerate.
- When the price is above the Kumo (cloud), the Kumo serves as a potential support zone.
- Conversely, when the price is below the Kumo, it functions as a potential resistance zone.
- Future Cloud Projections: Traders closely monitor the future projections of the Kumo, formed by Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B. These projections can provide valuable insights into potential trend directions.
- If Senkou Span A is projected above Senkou Span B, it indicates a bullish (upward) trend projection.
- Conversely, if Senkou Span B is projected above Senkou Span A, it suggests a bearish (downward) trend projection.
Understanding the Senkou Span’s role in the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator equips traders with a dynamic tool to assess potential price levels, support and resistance zones, and future trend directions. It adds depth and context to the analysis, making it an essential component of the comprehensive Ichimoku system.
Now, let’s explore the final piece of the puzzle, the Ichimoku Cloud Components, to grasp how they all come together to elevate your forex trading success.
Chikou Span
In the realm of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, the Chikou Span, often referred to as the Lagging Span, plays a unique role by offering a retrospective view of price action. It is essentially the closing price of the current candlestick, but it’s plotted 26 periods back on the chart. This seemingly backward-looking component is a valuable tool for traders seeking to uncover historical insights and validate trading signals.
How to Use Chikou Span:
- Trend Reversal Identification: One of the primary utilities of the Chikou Span is its ability to help identify potential trend reversals. By comparing the Chikou Span’s position relative to past price action, traders can gain critical insights into the market’s sentiment.
- When the Chikou Span crosses above past price action, it may indicate a potential bullish reversal.
- Conversely, when the Chikou Span crosses below past price action, it might signify a potential bearish reversal.
- The Chikou Span essentially serves as a “confirmation” tool that aligns with the Ichimoku system’s holistic approach to trading.
- Confirmation of Signals: The Chikou Span is often used in conjunction with other Ichimoku components to confirm trading signals. For instance, if the Tenkan Sen and Kijun Sen generate a crossover signal, traders may look to the Chikou Span to validate the signal by ensuring that it aligns with historical price action.
- If the Chikou Span supports the crossover signal by showing that it is in harmony with past price movements, it can boost the trader’s confidence in the validity of the signal.
- This confirmation aspect of the Chikou Span enhances the reliability of trading decisions.
In essence, the Chikou Span acts as a historical reference point, allowing traders to gauge the effectiveness of trading signals and identify potential trend reversals. Its unique role in the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator adds an extra layer of insight to the analysis, making it a valuable component for traders seeking to elevate their forex trading success.
Now that we’ve explored each of the key components of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator in detail, it’s time to bring it all together and understand how these components interact to guide your trading decisions.
Trading with Ichimoku Cloud
With a solid grasp of the Ichimoku Cloud components, it’s time to embark on a journey of practical application. Let’s explore how to harness the power of this formidable indicator to enhance your forex trading strategies and elevate your chances of success in the dynamic world of currency trading.
Identifying Trends with Precision
One of the primary objectives of the Ichimoku Cloud is to provide traders with a precise means of identifying trends in the market. It’s the first step toward making informed trading decisions. Here’s how you can leverage the Ichimoku Cloud for trend identification:
- Bullish Trends: When the market is in a bullish trend, you’ll notice that the price is positioned above the Kumo, the cloud-like area on the Ichimoku chart. In addition to this, both Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B should be pointing upwards. This combination of factors signals a robust bullish sentiment, indicating potential opportunities for long positions.
- Bearish Trends: Conversely, when the market is in a bearish trend, the price tends to reside below the Kumo. Moreover, both Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B slope downwards. This alignment suggests a strong bearish sentiment, highlighting the possibility of profitable short positions.
- Sideways Markets: In scenarios where the market is moving sideways, the price tends to oscillate within the Kumo, and both Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B remain relatively flat. This indicates a lack of a clear trend, signaling the need for caution and a focus on alternative trading strategies such as range trading.
Unveiling the Power of Support and Resistance
The Kumo, which forms the heart of the Ichimoku Cloud, serves as a dynamic support and resistance zone. It’s a critical aspect of the Ichimoku system that can significantly influence your trading decisions:
- Support in Bullish Trends: When the price resides above the Kumo, the cloud acts as a support level. This means that during bullish trends, if the price experiences a temporary pullback and approaches the Kumo, it’s likely to find support in this zone, potentially presenting an attractive entry point for long positions.
- Resistance in Bearish Trends: Conversely, in bearish trends where the price is below the Kumo, the cloud transforms into a resistance level. Should the price attempt to rally and approach the Kumo, it’s expected to encounter resistance. This resistance zone can be a compelling area for considering short positions.
Seizing Entry and Exit Opportunities
The Ichimoku Cloud’s components generate a variety of signals that serve as valuable guides for making entry and exit decisions:
- Tenkan Sen and Kijun Sen Crossovers: Pay close attention to the interaction between the Tenkan Sen and Kijun Sen lines. A bullish signal occurs when the Tenkan Sen crosses above the Kijun Sen, suggesting a potential upward movement in prices. Conversely, a bearish signal emerges when the Tenkan Sen crosses below the Kijun Sen, indicating a possible downtrend. These crossovers can guide your entry and exit points with precision.
- Kumo Breakout: Keep an eye on price movements concerning the Kumo. A breakout from the Kumo can signify a substantial shift in market sentiment and a potential trend reversal. If the price breaks out of the Kumo, consider it as a compelling entry signal.
- Chikou Span Confirmation: The Chikou Span, often referred to as the Lagging Span, plays a vital role in confirming signals generated by other Ichimoku components. When the Chikou Span aligns with a bullish or bearish trend, it strengthens the signal’s credibility. This confirmation aspect enhances your confidence in the validity of trading decisions.
In essence, the Ichimoku Cloud is not just a technical indicator; it’s your roadmap to navigating the complexities of the forex market. By effectively utilizing its components to identify trends, gauge support and resistance levels, and seize entry and exit opportunities, you can elevate your forex trading success to new heights. The Ichimoku Cloud becomes your guiding light through the ever-shifting terrain of currency trading, helping you make well-informed decisions and capture profitable trading opportunities.
Now that you’ve mastered the essentials of trading with the Ichimoku Cloud, let’s delve deeper into specific strategies and practical tips for incorporating this powerful indicator into your forex trading arsenal.
Ichimoku Cloud Trading Strategies
With a firm grasp of the Ichimoku Cloud’s components and their role in forex analysis, it’s time to delve into specific trading strategies that can help you harness the full potential of this indicator. Whether you’re a novice trader seeking guidance or an experienced trader looking to refine your approach, these Ichimoku Cloud strategies can elevate your forex trading success.
Riding the Trend with Confidence
Trend Following Strategy:
Trend following is a widely adopted strategy among Ichimoku Cloud enthusiasts. It enables traders to capitalize on sustained market trends with precision. Here’s how to implement this strategy:
- Identify the Trend: Begin by observing the Ichimoku Cloud and its components. Look for a clear bullish or bearish trend as indicated by the cloud and its various elements.
- Execute Entry: To enter a trade in the direction of the trend, wait for the Tenkan Sen to cross either above (for a bullish trend) or below (for a bearish trend) the Kijun Sen. This crossover serves as a strong initial signal.
- Trail the Trade: Once you’re in the trade, use the cloud itself as a trailing stop. Stay in the trade as long as the cloud remains aligned with the prevailing trend. This trailing stop strategy allows you to maximize gains as the trend continues.
Seizing Opportunities with Kumo Breakouts
Kumo Breakout Strategy
The Kumo breakout strategy is designed to capture significant price movements as they emerge from the cloud. It’s a powerful technique for identifying potential trend reversals or accelerations. Here’s how it works:
- Wait for the Breakout: Exercise patience as you observe the price’s interaction with the Kumo (cloud). Your objective is to wait for a convincing breakout from the cloud in the direction of the prevailing trend.
- Execute the Trade: Once the price successfully breaks out of the cloud, consider it a compelling entry signal. Enter a trade in alignment with the breakout direction, whether it’s bullish or bearish.
- Utilize Ichimoku Elements: As the trade progresses, leverage other Ichimoku components such as the cloud itself or the Chikou Span. These elements can serve as potential support or resistance levels, aiding in trade management.
Crossovers for Clarity
Senkou Span Cross Strategy
The Senkou Span cross strategy leverages the interaction between Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B to generate valuable trading signals. It enhances the clarity of trends and potential reversals. Here’s how to apply this strategy:
- Bullish and Bearish Signals: Keep a keen eye on the crossover of Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B. When Senkou Span A crosses above Senkou Span B, it generates a bullish signal, indicating potential upward momentum. Conversely, when Senkou Span A crosses below Senkou Span B, it generates a bearish signal, signaling potential downward pressure.
- Confirmation through Integration: While the Senkou Span cross is a robust signal on its own, consider integrating it with other Ichimoku signals for added confirmation. This approach enhances the reliability of your trading decisions.
Incorporating these Ichimoku Cloud strategies into your forex trading toolkit can provide you with a significant edge in the market. Whether you prefer trend following, breakout strategies, or crossovers, the Ichimoku Cloud offers a versatile set of tools to enhance your trading success. As you gain experience, remember that practice and continuous learning are key to mastering these strategies and adapting them to various market conditions.
In the world of forex trading, knowledge, and strategy are your allies. With the Ichimoku Cloud as your guide, you’re equipped to navigate the complex and dynamic landscape of currency trading with confidence and precision.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
As you embark on your journey to master the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator and elevate your forex trading, it’s crucial to be aware of common missteps that traders often encounter. Avoiding these pitfalls can help you harness the full potential of this powerful tool and enhance your trading success.
Overcomplicating Strategies – Keep It Simple
One of the prevalent mistakes traders make when incorporating the Ichimoku Cloud is overcomplicating their trading strategies. While it’s tempting to use numerous indicators or intricate approaches in conjunction with the Ichimoku Cloud, simplicity often proves to be more effective. Overloading your strategy with too many elements can lead to confusion and clouded judgment.
Tip: Stick to the fundamental principles of Ichimoku analysis. Focus on mastering the core components of the indicator and understanding their interactions. A clear and straightforward approach can yield more consistent results.
Ignoring Risk Management – Safeguard Your Capital
In the pursuit of profits, traders sometimes neglect proper risk management, which is a critical aspect of successful trading. Ignoring risk management can expose your trading capital to unnecessary hazards. To mitigate this, always implement sound risk management techniques:
- Set Stop-Loss Orders: Determine stop-loss levels for each trade to limit potential losses. These orders act as a safety net, ensuring that you exit a trade if it moves against you beyond a predefined point.
- Manage Position Sizes: Avoid overcommitting your capital to a single trade. Define the appropriate position size based on your risk tolerance and the size of your trading account. Diversify your trades to spread risk.
Tip: Prioritize capital preservation alongside profit generation. A disciplined approach to risk management is essential for long-term success in forex trading.
Neglecting Market Context – Look Beyond Ichimoku Signals
While the Ichimoku Cloud provides valuable insights into price trends and potential reversals, it’s essential to consider the broader market context. Neglecting economic events, geopolitical factors, and overall market sentiment can hinder your trading analysis.
Tip: Integrate Ichimoku signals with a comprehensive understanding of the market environment. Stay informed about global economic trends and significant news events that could impact your trades. A well-rounded analysis considers both Ichimoku signals and the broader context.
By steering clear of these common mistakes and adhering to best practices, you can optimize your use of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator. Keep your trading strategy straightforward, prioritize risk management, and maintain awareness of the broader market landscape. With these principles in mind, you’re better equipped to navigate the forex market successfully and elevate your trading endeavors to new heights.
Advanced Ichimoku Techniques
As you become more proficient in your forex trading journey, it’s essential to explore advanced Ichimoku techniques that can take your trading prowess to the next level. These strategies are designed for experienced traders who are well-acquainted with the basics of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator. Let’s delve into these advanced techniques and how they can enhance your trading strategies:
Multiple Timeframe Analysis – Gain a Comprehensive View
Advanced traders often employ multiple timeframe analysis when using the Ichimoku Cloud. This approach involves applying Ichimoku on various timeframes simultaneously. By doing so, you can confirm signals and gain a more comprehensive perspective on the market’s direction.
For instance, if you identify a bullish signal on the daily chart, you can cross-verify it with the Ichimoku analysis on shorter timeframes, such as the 4-hour or 1-hour charts. If these lower timeframes also exhibit bullish signals, it adds more weight to your trading decision.
Customized Settings – Tailor Ichimoku to Your Needs
Experienced traders understand that not all currency pairs or timeframes behave the same way. To adapt to varying market conditions, you can experiment with customized settings for the Ichimoku components.
For example, you can adjust the parameters for the Tenkan Sen, Kijun Sen, or Senkou Span to better suit specific currency pairs or timeframes. Customization allows you to fine-tune the indicator’s sensitivity, making it more responsive to the nuances of different markets.
Combining with Other Indicators – Strengthen Your Strategy
To create more robust trading strategies, advanced traders often combine the Ichimoku Cloud with other technical indicators. This synergy provides a comprehensive view of the market and enhances the accuracy of trading signals.
You can pair the Ichimoku Cloud with indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI), Moving Average Convergence Divergence (MACD), or the Fibonacci retracement levels. These combinations allow you to corroborate Ichimoku signals with additional confirmation from other indicators.
Tip: While combining indicators can strengthen your strategy, be cautious not to overcrowd your charts with too many elements. Maintain a balance between simplicity and effectiveness.
In conclusion, advanced Ichimoku techniques offer experienced traders valuable tools to elevate their forex trading endeavors. Multiple timeframe analysis provides a broader perspective, customized settings adapt to specific market conditions, and combining with other indicators strengthens your overall strategy. As you delve into these advanced strategies, remember that continuous learning and practice are key to mastering the art of Ichimoku Cloud trading.
Benefits and Limitations
The Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, with its multifaceted components and unique approach to technical analysis, offers traders a wide range of benefits. However, like any tool, it also has its limitations. To make the most of this powerful indicator, it’s crucial to understand both its advantages and shortcomings. Let’s explore the benefits and limitations of the Ichimoku Cloud:
Benefits of Using the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator
- Holistic View of Market Trends: One of the standout advantages of the Ichimoku Cloud is its ability to provide traders with a holistic view of market trends. It accomplishes this by considering various aspects of price action, such as support, resistance, and momentum. This comprehensive perspective helps traders make more informed decisions.
- Clear Entry and Exit Signals: The Ichimoku Cloud excels in generating clear entry and exit signals. Whether you’re a novice or experienced trader, the indicator’s components offer distinct cues on when to enter a trade, where to set stop-loss orders, and when to take profits. This clarity enhances the precision of your trading strategies.
- Dynamic Support and Resistance Levels: The Kumo, or cloud, formed by the Ichimoku Cloud’s Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B, acts as dynamic support and resistance levels. These levels adapt to changing market conditions, providing valuable insights into potential price reversals. Traders can use the cloud to identify key areas of interest.
- Suitable for Various Timeframes and Currency Pairs: Versatility is another hallmark of the Ichimoku Cloud. It’s applicable to a wide range of timeframes, from intraday trading to long-term investing. Additionally, this indicator is not limited to specific currency pairs, making it accessible to traders in different markets.
Limitations of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator
- Learning Curve: The Ichimoku Cloud Indicator has a relatively steep learning curve. Due to its multifaceted components and unique terminology, beginners may find it challenging to grasp initially. However, with dedication and practice, traders can overcome this hurdle.
- Conflicting Signals in Ranging Markets: While the Ichimoku Cloud excels in trending markets, it can generate conflicting signals in ranging or sideways markets. Traders may receive mixed cues that make it harder to determine market direction during such conditions. In these scenarios, additional analysis techniques may be needed for confirmation.
- Not a Standalone Solution: The Ichimoku Cloud should not be used as a standalone solution for trading decisions. While it offers a holistic view of the market, it’s essential to complement it with other analysis techniques, such as fundamental analysis, market sentiment, or other technical indicators. Relying solely on the Ichimoku Cloud may lead to missed opportunities or erroneous decisions.
In conclusion, the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator is a robust tool that can significantly enhance your forex trading strategies. Its benefits include providing a comprehensive market view, offering clear signals, and adaptability to various timeframes and currency pairs. However, traders should be aware of its learning curve, potential challenges in ranging markets, and the importance of using it alongside other analysis techniques. With proper understanding and practice, the Ichimoku Cloud can be a valuable ally in your trading journey.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator is a potent ally for forex traders seeking to elevate their success. By mastering its components and implementing effective strategies, you can navigate the complexities of the foreign exchange market with confidence. Remember to start with the basics, practice, and gradually incorporate advanced techniques to harness the full potential of this remarkable indicator. The Ichimoku Cloud is more than a technical tool; it’s a guiding star that can lead you to forex trading success.
Click here to read our latest article on Position Trading Strategies
FAQs
- What is the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, and how does it work? Answer: The Ichimoku Cloud Indicator, also known as Ichimoku Kinko Hyo, is a multifaceted technical analysis tool used in forex trading. It offers a holistic view of market trends by considering components such as Tenkan Sen, Kijun Sen, Senkou Span, and Chikou Span. These components provide insights into price momentum, support/resistance, and trend identification.
- How can the Ichimoku Cloud help me identify trends in the forex market? Answer: The Ichimoku Cloud is excellent at identifying trends. In a bullish trend, the price is above the Kumo (cloud), and both Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B point upwards. In a bearish trend, the price is below the Kumo, and both Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B slope downwards. In a sideways market, the price moves within the Kumo, and Senkou Span A and Senkou Span B are flat.
- What is the significance of the Kumo (cloud) in Ichimoku analysis? Answer: The Kumo serves as dynamic support and resistance levels in Ichimoku analysis. When the price is above the Kumo, it acts as a support level, and when the price is below, it becomes a resistance level. Traders often use the Kumo to identify potential areas for entry, exit, and stop-loss placement.
- How do I use the Tenkan Sen and Kijun Sen crossovers for trading signals? Answer: A bullish signal occurs when Tenkan Sen crosses above Kijun Sen, indicating a potential upward trend. Conversely, a bearish signal occurs when Tenkan Sen crosses below Kijun Sen, suggesting a potential downward trend. Traders use these crossovers to make informed entry and exit decisions.
- What role does the Chikou Span play in Ichimoku analysis? Answer: The Chikou Span, or Lagging Span, provides insights into historical price action. Its position relative to past price action can help identify potential trend reversals. Traders often use Chikou Span to confirm signals generated by other Ichimoku components.
- Are there specific trading strategies that can be applied with the Ichimoku Cloud? Answer: Yes, several trading strategies can be implemented with the Ichimoku Cloud. These include trend following, Kumo breakout, and Senkou Span cross strategies. Each strategy is designed to capitalize on different aspects of the Ichimoku components.
- What are some common mistakes to avoid when using the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator? Answer: Common mistakes include overcomplicating strategies by using too many indicators, neglecting risk management techniques, and failing to consider the broader market context and economic events alongside Ichimoku signals.
- Are there advanced techniques for experienced traders using the Ichimoku Cloud? Answer: Experienced traders can explore advanced techniques such as multiple timeframe analysis, customized settings for Ichimoku components, and combining Ichimoku with other technical indicators to create more robust trading strategies.
- What are the primary benefits of using the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator? Answer: The Ichimoku Cloud provides a holistic view of market trends, offers clear entry and exit signals, acts as dynamic support and resistance levels, and is suitable for various timeframes and currency pairs.
- What are the limitations of the Ichimoku Cloud Indicator? Answer: Limitations include a learning curve for beginners, potential conflicting signals in ranging markets, and the need to use it alongside other analysis techniques since it’s not a standalone solution for trading decisions.